Exploring Blood Plasma: A Vital Fluid
Blood is an essential fluid running through our veins, delivering oxygen and nutrients to every cell in our body. At the heart of this intricate system is plasma, the liquid component that carries cells and other substances. It is pivotal in maintaining our body's equilibrium and ensuring optimal health.
Therefore, understanding the role and significance of plasma in the blood is vital to comprehending various physiological and pathological processes.
In this blog, we will learn about blood plasma, its significance in health and medicine, and tools for analyzing it.
What is Blood Plasma?
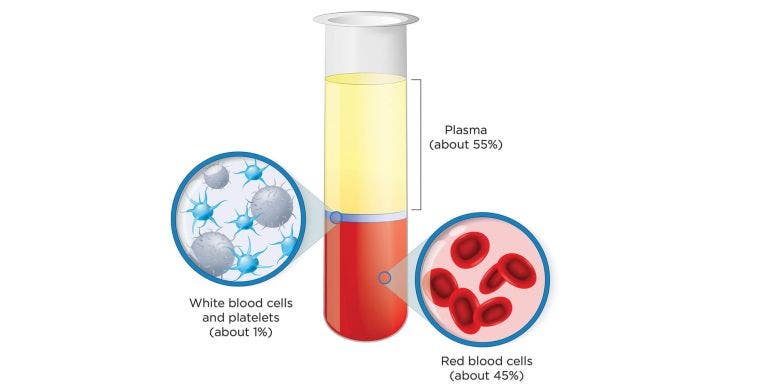
Blood plasma is the yellowish liquid component of blood that holds the blood cells in whole blood in suspension. It constitutes about 55% of total blood volume and maintains homeostasis in the body. This fluid contains water, salts, enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins.
Plasma is more than just a carrier. It transports nutrients, hormones, and waste products between different body parts. Additionally, it helps clotting and fights off infections, making it a vital player in our overall health.
How Does Plasma Differ From Other Blood Components?
Plasma is different from other blood components in various ways. Unlike other blood components, such as blood cells and platelets, plasma contains water, salts, enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins.
Its primary function is to transport the other blood components throughout the body, along with nutrients, waste products, and hormones. While red and white blood cells and platelets carry out specific functions in immunity, oxygen transport, and clotting.
However, without the plasma blood, these cells would not be able to travel and perform their functions effectively.
Role of Blood Plasma in Medical Applications
Plasma has therapeutic applications. It can be used in treatments such as plasma exchange for patients with autoimmune diseases or in producing clotting factors for hemophilia patients.
The following points explain the role of blood plasma in medical applications:
Clotting Factors
Plasma contains proteins known as clotting factors, which are essential for blood clotting. It's used in the treatment of hemophilia and other clotting disorders.
Burn and Shock Treatment
The plasma expands blood volume, making it a critical treatment for patients with extensive burns or those in shock.
Immune Support
Plasma contains antibodies, providing a boost to the immune system. It's used in treatments for immune deficiencies.
Chronic Conditions
Plasma-derived products can treat chronic conditions such as Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
COVID-19 Treatment
Convalescent plasma has been utilized to treat COVID-19, with plasma taken from recovered patients containing antibodies against the virus.
Nutrient Carrier
Plasma carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products to and from different body parts, which is essential for general health.
Albumin Replacement
Albumin, a protein in plasma, is used in the treatment of liver disease, kidney dialysis, and surgical procedures to balance fluid levels in the body.
Hyperimmune Globulins Production
Plasma is used to create hyperimmune globulins to prevent diseases such as rabies, hepatitis, and tetanus.
Blood plasma, with its multiple roles, plays a crucial part in modern medicine. With advances in science, the potential uses of plasma in medicine continue to grow.
The Importance of Donating Plasma
Plasma donation is a crucial act that can save lives. Donated plasma is used to treat various conditions, from burns and shock to liver disease and clotting disorders. The donation process is relatively simple and safe, yet the impact it can have on someone's life is profound. By donating plasma, individuals not only contribute to the immediate health needs of others but also support ongoing medical research, fostering advancements in healthcare that benefit society as a whole.
Lab Equipment for Analyzing Blood Plasma
Analyzing plasma is crucial in both clinical diagnostics and research. Various lab devices are designed to assess different components and properties of plasma in blood.
The following are the devices used for plasma analysis:
Hematology Analyzer
This device provides a complete blood count (CBC), including details about red and white blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets. While its main focus is on cellular components, the readings can indirectly give insights into the plasma by calculating the plasma volume based on hematocrit.
Coagulation Analyzer
This instrument evaluates plasma's clotting properties. It's used to diagnose bleeding disorders and monitor anticoagulation therapies.
Blood Chemistry Analyzer
This machine measures various chemical components in plasma, such as electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate), enzymes, and metabolites. It provides insights into organ function, metabolic status, and more.
Blood Gas Analyzer
A blood gas analyzer is used in critical care settings. This device measures pH, partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide, bicarbonate, and other parameters in arterial plasma to assess respiratory and metabolic status.
Electrophoresis Apparatus
This device separates proteins based on their size and charge. It's commonly used to analyze plasma proteins like albumin, globulins, etc.
Immunoassay Analyzers
Immunoassay analyzers measure specific proteins, hormones, drugs, and other molecules in plasma using antigen-antibody reactions.
Mass Spectrometers
Mass Spectrometers are advanced science education supplies that identify and quantify specific molecules in plasma samples based on their mass-to-charge ratio. They are especially valuable in toxicology and pharmacology.
Spectrophotometers
These devices measure the intensity of light absorbed by a sample. In plasma analysis, they can be used to quantify substances like bilirubin or to determine the concentration of specific proteins.
ELISA Readers
ELISA Readers are designed for the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method. These devices detect and measure substances such as antibodies, hormones, or peptides in plasma.
Microscopes
Microscopes are used in combination with specific staining techniques; they can reveal cellular abnormalities in the blood, which can indirectly provide information about plasma composition or conditions.
Therefore, when selecting a device for plasma analysis, it's essential to choose the one best suited for the specific components or properties of interest as each device has its unique uses.
In conclusion, blood plasma plays a crucial role in our health system. Its vast array of uses, from life-saving treatments in emergencies to long-term therapies for chronic conditions, underscores its significance. The ongoing research into its potentials, coupled with technological advancements, is continually broadening our understanding and capabilities within this field.
Are you curious about the intricate world of blood and its components? Dive deeper into the medical science world with West Lab Canada. We offer high-quality lab equipment to assist you in scientific research and experimentation.
Visit our website and shop for lab equipment today!