10 Tips to Improve Your Pipetting Technique
It is important to establish a proper pipetting technique as poor techniques can dramatically reduce the accuracy and performance of the pipettor. It is worth taking the time to fine-tune your technique to ensure you are working as efficiently and effectively as possible. We have compiled a list of the top 10 pipetting technique tips to assist you in achieving a great technique.
- Correct tips – The first tip, and probably the most obvious, is to ensure you are using the correct pipette tip. Most manufacturers of pipette tips will offer a compatibility chart such as the ISG® compatibility chart on our website. Incompatible pipette tips can reduce accuracy and precision so it is important that you choose a high-quality pipette tip suited to your pipette. Low retention tips are recommended for high accuracy.
- Pre-wetting – It is important that you pre-wet the pipette tip for a couple of reasons. Firstly, it allows you to flush out residual substances and prevent cross-contamination. Secondly, it increases the humidity resulting in less evaporation (evaporation can cause significant sample loss). To pre-wet the tip, simply draw and expel liquid fully at least three times before use.
- Pipetting angle – It is important to ensure you aspirate and dispense at the correct angles to ensure accuracy. Ensure you are aspirating at 90° and that you pull the pipette tip out of the centre of the container at 90° also. When dispensing, ensure you hold the pipette at an angle (10-45°). Working to these angles ensures the desired liquid amount is drawn into the tip properly and that all of the liquid is fully dispensed without leaving any residue in the tip.
- Dispensing – When dispensing the sample, it is important that you dispense pressing the tip to the side of the container or into the liquid already in the container. Make sure it is also at an angle as mentioned above. You should not dispense into direct air as this can affect your measurement results.
- Standard mode pipetting – Ensure you are using standard mode pipetting rather than reverse pipetting for the most accuracy and precision. Reverse pipetting can be used when you are working with viscous samples. If you use this reverse mode with normal fluids, the pipette will tend to deliver more than the desired volume. But if you were to use standard mode with viscous samples, however, you would receive less than the desired volume.
- Temperature – Believe it or not, the temperature is probably the most important factor that can influence a pipettes performance. The specifications provided for your pipette are often based on testing at room temperature (~20-25°C). If pipetting is performed at temperatures outside of this range, it can affect the amount of liquid dispensed.
- Ergonomics – A problem that can arise with individuals who use pipettes on a regular basis is Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) which occurs when the same physical exercise is performed in excess amounts. RSI from pipettes can cause some serious harm to users where they can experience muscle and joint pain. The most effective way to prevent RSI is to use an ergonomic pipette and focus on proper technique. The design of the pipette can have a significant impact on the comfort and safety of the user. Spend some time looking into the design of the potential pipette you are considering for purchase. A good pipette design will allow for neutral positioning of the hand and wrist. Here are some design aspects to consider:Balance – An ergonomic body with balanced weight distribution offers the greatest comfort for extended pipetting periods.
- Comfort – A well-contoured body shape ensures a perfect fit for all hand sizes.
- Versatility – Is the pipette suitable for both left and right-handed users?
- Plunger – Look for a plunger that is thumb-friendly with reduced plunger pressure. Also, look for comfortable thumb access where you don’t need to over-stretch the thumb.
- Tip Ejection – A good tip ejection system can reduce thumb workload by up to 70% easing the pressure on the thumb.
- Finger Hook – A good finger hook will be able to take the weight of the pipette for a more relaxed grip. Look for a comfortable and well-balanced finger hook which will reduce hand stress.
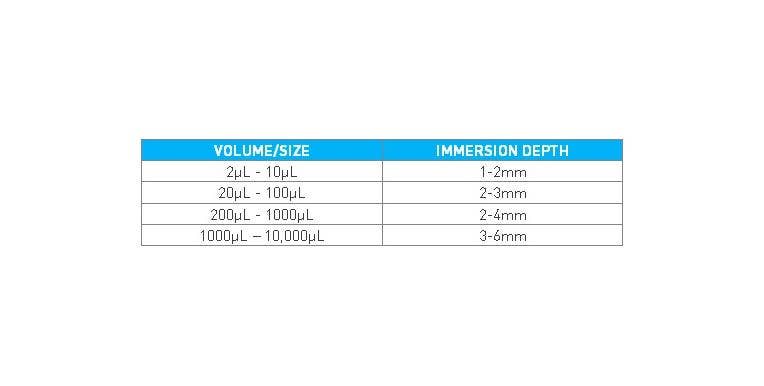
- Immersion – It is also important that you place the pipette tip into the sample at the proper immersion depth. Depending on the size/volume of the pipette, the immersion depth will change slightly. Incorrect immersion depth can result in incorrect sample volumes. Remember, keep the pipette as vertical as possible during this process.


- Plunging – When releasing the plunger during the aspiration process, do so at a controlled and consistent motion to increase both accuracy and precision. The pressure required will change based on the liquid being aspirated.
- Pausing – A simple tip that helps to minimise errors is to pause consistently after aspiration for about one or two seconds while the liquid is still in the pipette tip. This allows for the liquid in the tip to “bounce” when the plunger stops which simply gives the liquid time to stabilise.
Having a good pipetting technique will not only assist you with easing strain caused by repetitive use, but it will also ensure you drastically improve your accuracy and precision. The good technique also helps you keep your pipettes in excellent condition. It is ideal for your laboratory to develop standard operating procedures that all staff should follow. You should make sure all staff are trained to work on this standard.
Read also: How to reduce your plastic consumption and save money with pipette tips